Indian agribusiness is entering a pivotal phase of financial transformation. With agricultural credit forecasted to hit a record ₹32.5 lakh crore in FY26, up from ₹28.7 lakh crore in FY25, access to credit, especially working capital, is becoming more abundant and more critical than ever before. This surge in financing is helping farmers and agri-enterprises modernise operations, invest in advanced technologies, and withstand market volatility, laying the foundation for a resilient agribusiness sector in 2026.
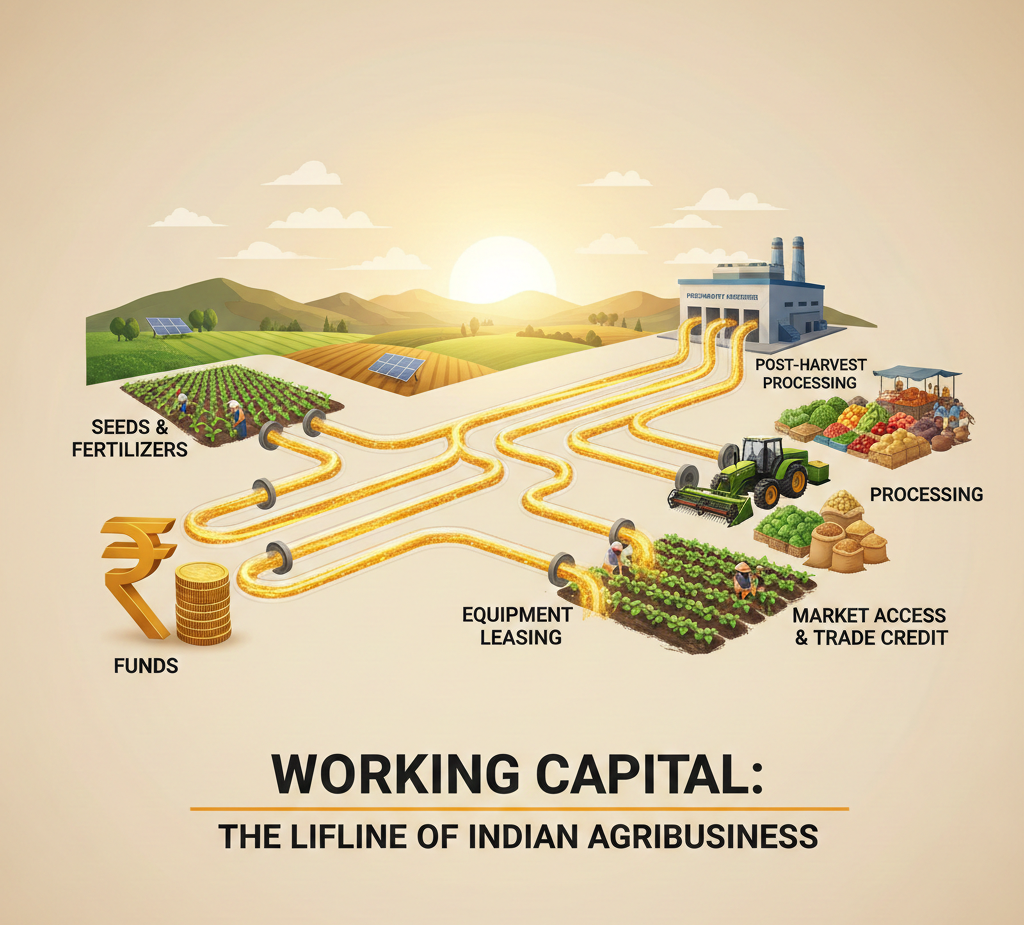
In this context, working capital isn’t just a financial metric but the lifeline that enables growth, innovation, and stability across agricultural value chains. From input procurement and labour costs to logistics and inventory, effective working-capital management determines how swiftly an agribusiness can respond to opportunities and challenges.

Importance of working capital
These are the funds available for everyday operations, which drive the engine of agribusiness. Unlike industrial sectors with predictable cash cycles, agriculture is highly seasonal. Expenses such as seeds, fertilisers, equipment hire, and workforce wages occur long before revenues from crop sales are realised. Without a smooth working capital flow, even high-potential enterprises can face delayed cash flows, squeezed profit margins, and limited growth.
For example, the Government of India’s Modified Interest Subvention Scheme (MISS) continues to support short-term loans through Kisan Credit Cards (KCCs), offering concessions explicitly aimed at working capital needs. Around 77 million KCCs are active, offering farmers access to subsidised credit at effective interest rates as low as 4 %, thereby enhancing short-term liquidity.
Despite these positive trends, credit distribution remains uneven across regions, and many agribusinesses still struggle to bridge cash flow gaps, underscoring the importance of strategic capital management.
Better working capital can transform agribusinesses in 2026
Here’s how improved access and management will reshape the sector in the year ahead:
- Ensuring operational continuity and growth: This ensures that routine expenses, from seed purchases to harvesting logistics, are met without borrowing at high rates or disrupting production schedules. With sufficient capital, agribusinesses can plan ahead, participate in competitive markets, and negotiate bulk discounts with suppliers.
- Fueling technology adoption and efficiency: In 2026, digital and precision farming tools are increasingly central to competitiveness. Technologies like soil sensors, drone monitoring, and automated irrigation improve yields and reduce costs. However, deploying these innovations often requires upfront investment. Adequate capital enables agribusinesses to adopt such technologies without compromising liquidity.
- Supporting value-added and SME segments: Value-added players, from cold storage operators to food processors, face longer cash-conversion cycles due to inventory storage, grading, and quality clearance procedures. Tailored working capital solutions help these agribusiness SMEs cover operating costs and maintain production quality while navigating fluctuations in market demand.

- Enhancing market access and exports: India’s agri-exports are poised for expansion in 2026, backed by government initiatives and infrastructure support. Enterprises with strong working capital positions can better navigate export cycles, secure international contracts, and manage seasonal price fluctuations. Flexible capital also enables participation in futures markets, enhancing price discovery and risk management.
- Building resilience to market and climate risks: Agriculture remains vulnerable to climatic unpredictability and price swings. Better capital provides a buffer against adverse weather events and crop failures, enabling agribusinesses to withstand shocks without compromising future productivity.
Agriwise supports working capital needs
At this juncture, Agriwise is reshaping how agribusinesses access finance. Agriwise specialises in tailored agricultural financing solutions that go beyond traditional credit products. They offer short-term working capital loans, term loans, and commodity-linked financing designed explicitly for agri-enterprises, enabling smoother cash flows and better financial planning.
Unlike generic lending options, Agriwise understands the unique cash flow cycles of the farm and allied sectors. By combining deep agricultural insights with flexible financing products, Agriwise empowers businesses to optimise working-capital utilisation, bridge seasonal gaps, and invest in growth opportunities. This kind of nuanced financing support is especially critical in 2026, as agribusinesses scale, innovate, and compete both domestically and globally.

Practical strategies for managing capital
To harness the full potential of working capital, agribusinesses should embrace a mix of financial discipline and smart tools:
- Accurate cash-flow forecasting: Predict peaks and troughs in expenses and revenues to avoid liquidity crunches.
- Digital lending platforms: Use fintech and agri-finance solutions that offer fast approval and tailored working-capital loans.
- Optimised inventory management: Reduce excess stock and align purchases with market cycles.
- Government credit programmes: Use initiatives like KCCs and interest subvention schemes to reduce borrowing costs.
- Strong banking relationships: Maintain robust interactions with lenders to facilitate better credit access when needed.
The future of agribusiness in 2026
As India cements its position as a global agrarian powerhouse, effective working-capital management will differentiate successful agribusinesses from the rest. As financial inclusion increases and credit products become more tailored and accessible, the focus should shift from merely accessing funds to strategically managing them.
Working capital will not just support daily operations; it will fuel innovation, strengthen resilience, and unlock new markets. Agribusinesses that prioritise efficient capital practices in 2026 will be well-placed to lead India’s agricultural growth story, sustainably and profitably.
FAQs:
- What is working capital in agribusiness, and why is it important?
Working capital in agribusiness refers to the funds used for day-to-day operations such as buying inputs, paying labour, managing logistics, and storing produce. It is important because agriculture involves seasonal cash flows, and timely access to cash ensures uninterrupted operations and higher productivity.
- How does better working capital improve agribusiness profitability?
Better capital enables agribusinesses to procure quality inputs on time, reduce reliance on high-interest informal loans, and manage inventory more efficiently. This leads to improved yields, lower operational costs, and stronger margins over the production cycle. - What are the typical working capital challenges faced by agribusinesses?
Agribusinesses often face delayed payments, long cash-conversion cycles, rising input costs, and seasonal income gaps. Limited access can restrict growth, delay technology adoption, and increase financial stress during critical periods. - How can agribusinesses improve working capital management in 2026?
In 2026, agribusinesses can improve capital management by accurately forecasting cash flows, using digital and agri-focused financing platforms, optimising inventory levels, and leveraging government credit schemes for short-term agricultural finance. - How does Agriwise help agribusinesses meet their working capital needs?
Agriwise provides customised financial solutions tailored to the agricultural sector, including short-term loans and commodity-linked financing. By understanding seasonal cycles and operational needs, Agriwise helps agribusinesses maintain liquidity, manage cash flows efficiently, and scale sustainably.
Disclaimer
The content published on this blog is provided solely for informational and educational purposes and is not intended as professional or legal advice. While we strive to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information presented, Agriwise make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, suitability, or availability with respect to the blog content or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained in the blog for any purpose. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk. Readers are encouraged to consult qualified agricultural experts, agronomists, or relevant professionals before making any decisions based on the information provided herein. Agriwise, its authors, contributors, and affiliates shall not be held liable for any loss or damage, including without limitation, indirect or consequential loss or damage, or any loss or damage whatsoever arising from reliance on information contained in this blog. Through this blog, you may be able to link to other websites that are not under the control of Agriwise. We have no control over the nature, content, and availability of those sites and inclusion of any links does not necessarily imply a recommendation or endorsement of the views expressed within them. We reserve the right to modify, update, or remove blog content at any time without prior notice.