Did you know that the crops sitting in a warehouse could actually earn you money before they’re even sold? That’s the power of Warehouse Receipt Financing.
Financial institutions are expected to meet the agriculture credit target of Rs 32.5 lakh crore for 2025–26.
By turning stored produce into collateral, farmers and agri-traders can access instant credit, avoid distress sales, and even sell at the most profitable time. This financial tool is helping stakeholders protect their harvest, maximise returns, and step confidently into formal markets. In India, electronic Warehouse Receipts (e-NWRs) and regulated storage systems are now unlocking significant value for agricultural stakeholders by enabling stored commodities to be used as collateral for short-term loans. But what are those benefits?
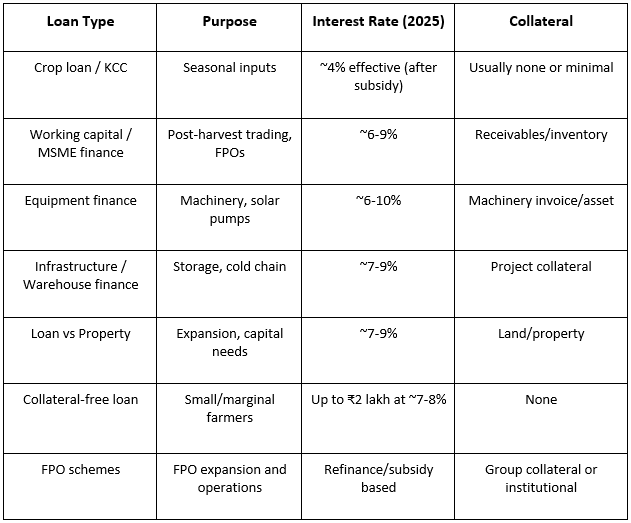
1. Improved access to working capital: One of the most immediate benefits of Warehouse Receipt Financing is the ability for farmers and traders to convert stored produce into cash without having to sell immediately. By pledging e-NWRs issued from registered warehouses/warehouse receipts by collateral managers, borrowers can access loans typically amounting to 70–75% of the commodity’s market value, helping manage input costs such as seeds, fertilisers, labour, and transport. This access to formal finance is significant in a sector where formal institutions historically offer less than 3% of agricultural credit in emerging markets.
2. Avoidance of distress sales & price timing advantage: Post-harvest periods often lead to oversupply, suppressing prices when farmers need cash the most. Warehouse Receipt Financing allows produce to be stored under certified conditions and sold later, capturing higher seasonal prices instead of resorting to low-price distress sales immediately after harvest.
For example, India’s food grain production in 2023-24 was approximately 330 million tonnes, but only about 1.24 million tonnes were financed via warehousing/e-NWR instruments, indicating huge untapped potential for price optimisation through timely selling.

3. Reduced post-harvest losses and quality preservation: Certified warehouses, governed by the Warehousing Development and Regulatory Authority (WDRA), ensure that stored commodities are graded, inspected, and preserved under optimal conditions. Proper storage reduces waste, maintains quality, and allows farmers to fetch better prices later in the season. Without access to formal warehousing and finance, farmers face significantly higher spoilage rates, up to 30–40% in unregulated storage systems worldwide.
4. Strengthened bargaining power & market participation: By delaying sales and leveraging formal receipts, farmers and agri-traders gain stronger bargaining power in the market. Instead of selling to local brokers at low prices, they can reach broader markets, including institutional and export channels, often resulting in better price realisation and income stability. Warehouse Receipt Financing also encourages farmers to become “price setters” rather than “price takers”, as they have the flexibility to choose when and where to sell.
5. Formal credit history and lower reliance on informal lending: By engaging with formal WRF mechanisms, farmers and traders build a credit history that can open the door to future loans on favourable terms. e-NWR-based financing also helps reduce reliance on informal moneylenders, who typically charge exorbitant interest rates, thereby improving the overall financial health of agrarian communities.
Moreover, WRF helps lenders better assess risk through verified commodity collateral, often resulting in competitive interest rates and structured repayment terms.

Warehouse receipt industry figures that matter
- India’s regulated warehouse capacity reached approximately 44.8 million tonnes by March 2025, signalling expanding storage infrastructure.
- Electronic Warehouse Receipts (e-NWRs) were issued for roughly 54 million metric tonnes of agricultural commodities, indicating growing adoption of digital instruments.
- The warehouse receipt financing ecosystem, including negotiable receipts, was valued at around ₹35,000 crore in recent years, demonstrating substantial credit flows into agriculture.
- Commodity valuations backed by storage receipts surged from ₹12,362 crore in FY23 to nearly ₹19,930 crore in FY25, reflecting institutional confidence and market growth. Based on current growth momentum, commodity valuations are expected to cross 24,000–26,000 crore in FY26.
How Agriwise helps farmers & agri-traders
At Agriwise, we empower farmers, traders, and agri-businesses to unlock the full potential of Warehouse Receipt Financing through a comprehensive suite of services:
- Access to WHR (Warehouse Receipt) finance: Agriwise Finserv provides tailored financing solutions against warehouse receipts issued by the collateral manager (CM), ensuring borrowers get the cash they need without distress selling.
- Wide network of accredited warehouses: We partner with Asia’s leading warehousing & collateral management company (Staragri).
- Market insights & advisory: Our platform gives real-time price trends, market data, and sell timing guidance, helping clients maximise returns on stored commodities.
- Technology-driven transparency: Digital documentation and tracking through secure systems enhance lender confidence and streamline loan approvals.
- Farmer education & support: From documentation help to training on using receipts and understanding loan terms, Agriwise bridges the gap between farmers and formal credit.

Conclusion
Warehouse Receipt Financing stands out as a powerful tool in modern agricultural finance, enabling farmers and agri-traders to stabilise incomes, avoid premature selling, and access formal credit with fewer hurdles. As India’s regulated warehousing ecosystem expands and digital receipts gain traction, WRF will play an increasingly pivotal role in strengthening rural economies and enhancing farm profitability. With partners like Agriwise, stakeholders can confidently leverage these financial instruments to grow sustainably and prosper in a competitive market.
FAQs
- What is Warehouse Receipt Financing (WRF)?
WRF is a credit facility that allows farmers or agri-traders to pledge stored commodities in certified warehouses/professional warehouses as collateral to access short-term loans. - Who can benefit from WRF?
Farmers, agri-traders, manufacturers, exporters, importers and agribusinesses who want timely working capital, better price realisation, and reduced post-harvest losses can benefit from WRF. - How does WRF help avoid distress sales?
By storing commodities in certified warehouses and using receipts as collateral for loans, farmers can wait for better market prices before selling immediately after harvest. - What types of commodities are eligible for WRF?
Grains, pulses, oilseeds, spices, and other non-perishable agricultural products stored in WDRA-approved or accredited warehouses can be financed under WRF. - How does WRF improve financial inclusion?
WRF builds formal credit history for farmers and traders, reducing reliance on informal lenders and enabling easier access to future loans at competitive interest rates.
Disclaimer
The content published on this blog is provided solely for informational and educational purposes and is not intended as professional or legal advice. While we strive to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information presented, Agriwise make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, suitability, or availability with respect to the blog content or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained in the blog for any purpose. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk. Readers are encouraged to consult qualified agricultural experts, agronomists, or relevant professionals before making any decisions based on the information provided herein. Agriwise, its authors, contributors, and affiliates shall not be held liable for any loss or damage, including without limitation, indirect or consequential loss or damage, or any loss or damage whatsoever arising from reliance on information contained in this blog. Through this blog, you may be able to link to other websites that are not under the control of Agriwise. We have no control over the nature, content, and availability of those sites and inclusion of any links does not necessarily imply a recommendation or endorsement of the views expressed within them. We reserve the right to modify, update, or remove blog content at any time without prior notice.