NBFCs refer to entities that are not banks but provide services such as lending and other activities without holding a banking license. One of the main reasons why people choose NBFCs over banks is due to lower costs. Since the need for finance in the farming community is on the rise, banks alone cannot cater to the increasing demand, so NBFCs provide finance to both the public and private sectors.
Entities such as banks consider a strong credit score an advantage while providing a loan and can be stringent regarding the documents’ approval.
Hence, most people turn towards NBFCs for business loans because of less documentation and competitive interest rates.
Let’s further look at the advantages of NBFCs over banks:
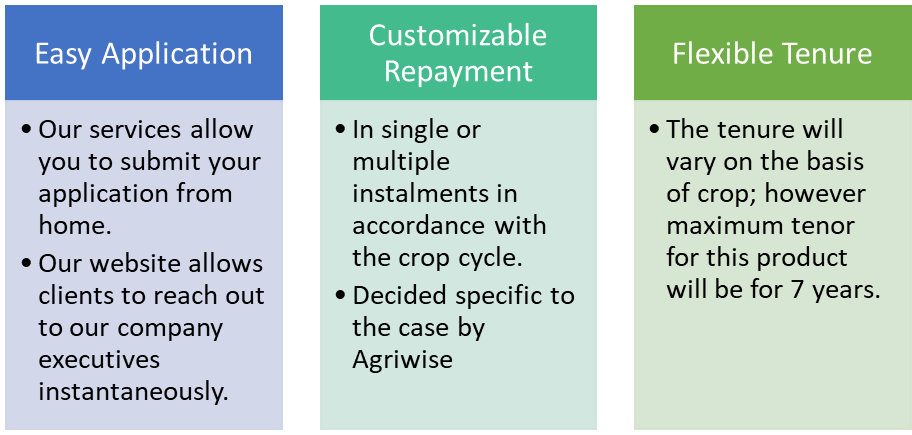
- NBFCs provide end-to-end solutions with an easy application process and instant approvals making the loan process faster than banks.
- NBFCs base interest rates are not regulated by the RBI. Therefore, have greater flexibility and offers competitive interest rates.
- NBFCs such as Agriwise provide exceptional customer service and require minimum documentation along with relatively lenient eligibility criteria compared to traditional banks, leading to quick disbursal of funds.
While computing the loan amount over the collateral property during calculation, NBFCs consider statutory changes like stamp duty, etc. Further, loan repayment is easier than banks owing to no penalty clauses.
With offerings that prioritize customers and provide hassle-free and digitized loan processes, the farming community prefers NBFCs over banks.
References:
- https://inc42.com/resources/heres-why-nbfcs-are-better-than-traditional-banks-for-business-loans/
- https://lawyerinc.net/learning/advantages-of-nbfc-over-bank/#:~:text=NBFC%20are%20more%20profitable%20than%20Banks%20because%20of,as%20banks%20have%20stringent%20regulations%20and%20cumbersome%20paperwork
- https://keydifferences.com/difference-between-nbfc-and-bank.html#Definition
- https://www.lendingkart.com/blog/banks-nbfc-which-better-business-loans/
- https://www.moneytap.com/blog/nbfcs-vs-traditional-banks/#Why_NBFCs_are_a_better_choice_for_personal_loans